Analysis of Recent Data Breach Surge in South Korea
Cybersecurity Experts Warn of Data Breach Surge
In recent weeks, South Korea has experienced a data breach surge that has heightened concerns among cybersecurity experts. Notably, this increase in cyber incidents aligns with South Korea’s prominent role in a significant cybersecurity debate at the United Nations Security Council (UNSC) in June. This situation underscores the intricate link between geopolitical events and cyberattacks, where major decisions or announcements can often trigger data breaches.
Context and Background
The United Nations Security Council is tasked with maintaining international peace and security, wielding powers such as peacekeeping, imposing sanctions, and authorizing military action. The presidency of the UNSC rotates monthly among its members. In June, South Korea, during its presidency, organized a high-level debate on cybersecurity to bolster the UNSC’s efforts in addressing cyber threats. This focus on cybersecurity has intensified due to the rise in cyber threats during the COVID-19 pandemic and the broader adoption of digital technologies.
Detailed Breach Information
The recent exposures have revealed various types of sensitive information, each posing unique risks:
Personal Information:
- Names
- Usernames
- Emails

- Passwords & Corporate Data
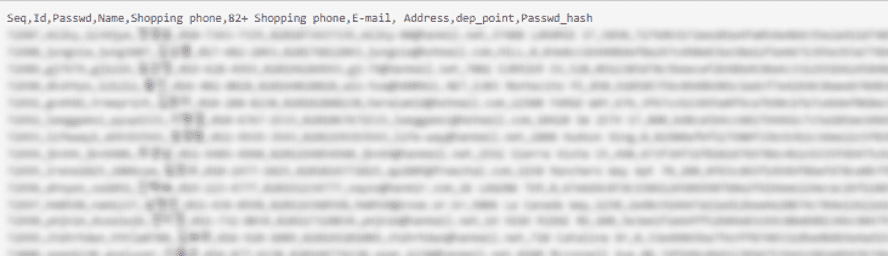
Contact Details:
- Birthdates
- Phone numbers
- Addresses

Data Breach Surge Attack Vectors

With the data found and mentioned in the previous section, different types of attacks can be carried out, depending on the type of exposed data:
- Phishing and Spear Phishing Attacks: Names, usernames, and emails can be used to craft targeted phishing emails. These emails deceive recipients into revealing more personal information, such as login credentials or financial details.
- Account Takeover: Exposed passwords, especially if reused across multiple sites, allow attackers to gain direct access to personal and corporate accounts. This can lead to unauthorized transactions, data theft, and further compromises.
- Social Engineering: Birthdates, phone numbers, and addresses provide attackers with the information needed to impersonate individuals or organizations, tricking targets into divulging sensitive information or performing actions that compromise security.
- Corporate Espionage: Company affiliation data can be used to identify key personnel and exploit organizational weaknesses. This can result in the theft of proprietary information, disruption of operations, or targeted attacks against specific companies.
- Network Attacks: IP addresses expose networks to unauthorized access and monitoring. Attackers can use this information to launch Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) attacks, spread malware, or conduct further breaches.
Tips to Protect Your Personal and Sensitive Information
- Enable Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Adding an extra layer of security for your accounts can help protect against unauthorized access, even if your password is compromised.
- Use Secure Networks: Avoid using public Wi-Fi to access or transmit sensitive information. Instead, use a secured or virtual private network (VPN) to enhance online privacy.
- Remove Unused Accounts: Regularly review and delete any accounts for no longer use services. Ensuring that your information is not stored unnecessarily reduces the risk of it being exposed to a breach.
By implementing these measures, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of falling victim to data breaches and better protect their sensitive information from cyber threats.

