Recent Data Breach at Ayesa: A Ransomware Case Study
Strengthening Defenses Against Ransomware Attacks
In recent years, ransomware attacks where criminals lock up a victim’s data and demand money to unlock it have become a serious threat to organizations worldwide. These attacks target many sectors, including healthcare and finance. The goal is often not just to make money but also to cause disruption and chaos. One group known for these aggressive tactics is Black Basta. They use a method called double extortion, where they not only lock the victim’s data but also threaten to release sensitive information unless they are paid. As these cybercriminals continue to improve their methods, it is increasingly important for organizations to strengthen their defenses.
The Ayesa Data Breach
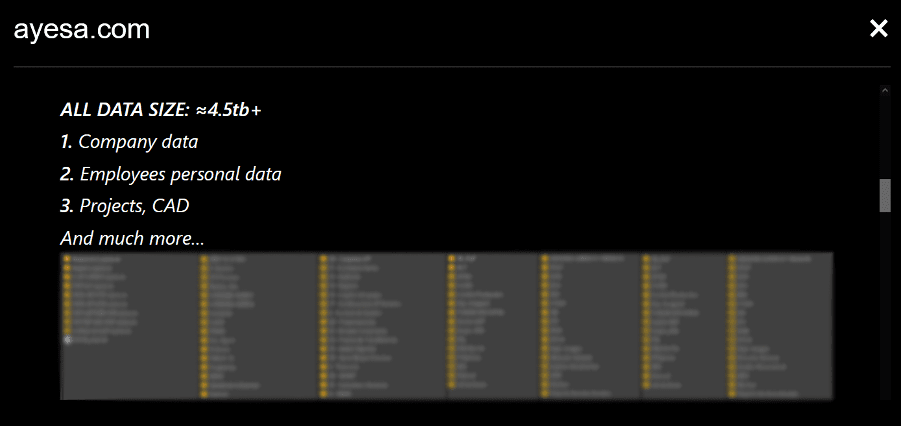
Ayesa, a leading Spanish company providing technology and engineering services, seems to have recently fallen victim to a potential ransomware attack by Black Basta. With over 12,500 employees and a presence in 23 countries, the possible breach at Ayesa highlights the extensive reach of these cyber criminals. The attack, which was made public on May 13, 2024, potentially resulted in the theft of about 4.5 terabytes of sensitive data, including:
- Company data (treasury, human resources, administration, general management, security, audits, etc.)
- Employees’ data
- Projects and CAD files
The Threat of Detailed Profiling
The types of data potentially stolen from Ayesa, such as personal details of employees and company information, can be highly valuable for criminals. With this information, threat actors can create synthetic identities to impersonate employees. These synthetic identities can then be used to commit fraud, purchase illicit items, or even access secure company systems by posing as legitimate employees. Additionally, cybercriminals can further enhance these synthetic identities by accessing the information available from data brokers. Data brokers collect and sell large amounts of personal information, often gathered from public sources such as social media profiles, past employment history, and other publicly available records. This information can be accessed by cybercriminals to enhance their profiling efforts significantly. Additionally, information from previous breaches can be cross-referenced to enrich these profiles further.
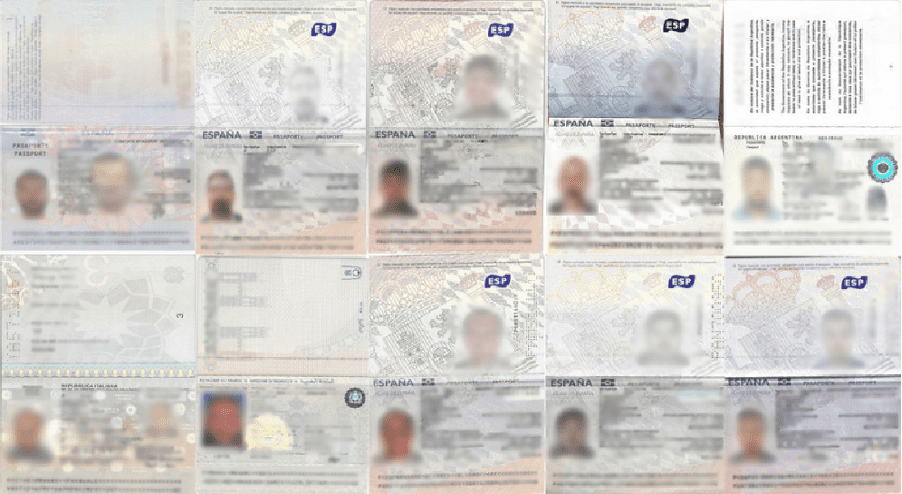

For example, if a cybercriminal obtains an employee’s name, job title, and contact information from Ayesa, they can look up additional details such as social media profiles, past employment history, and other personal records from data brokers. This enriched profile can then be used to craft highly targeted phishing emails or impersonation attempts, making the attacks more convincing and increasing the likelihood of success.

The Ease of Exploiting Leaked Data
Generative AI tools, especially those without ethical restrictions like WormGPT or FraudGPT, enable cybercriminals to automate and carry out more realistic and sophisticated fraudulent attacks.

These tools can write undetectable malware, create convincing phishing pages, and generate spear-phishing emails that appear to come from trusted sources within an organization. The ability of AI to exploit human psychology significantly increases the likelihood of successful cyberattacks.
Potential Attack Vectors
With the kind of data a cybercriminal can obtain from these data breaches, several attack vectors can be exploited:
- Identity Theft: Personal data such as ID card photos and employee information can be used to commit identity theft, leading to financial loss and reputational damage.
- Phishing and Social Engineering: Detailed personal and company data can help attackers craft convincing phishing emails, increasing the success rate of these attacks.
- Intellectual Property Theft: Projects and CAD files contain valuable intellectual property that malicious actors could exploit.
- Credential Stuffing: Access to employee credentials could allow attackers to gain unauthorized access to other systems where the same credentials might be used.
Cybersecurity Recommendations
In addition to the classical tips we have provided in previous blogs, such as enabling MFA, it is important to take additional steps to secure your devices and networks.
- Secure Your Devices: Ensure that any device used to access sensitive information is secured with updated antivirus software and a firewall. Regularly update your operating system and software to protect against vulnerabilities.
- Use Secure Networks: Avoid using public Wi-Fi to access or transmit sensitive information. Instead, use a secured or virtual private network (VPN) to enhance online privacy.
- Remove Unused Accounts: Review and delete any accounts for unused services regularly. Ensuring your information is not stored unnecessarily reduces the risk of being exposed to a breach.
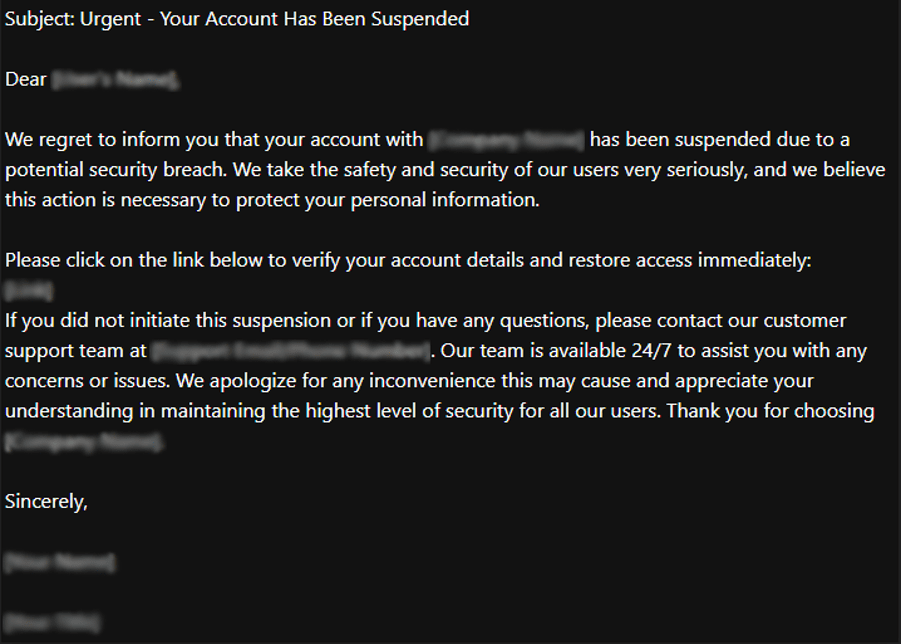
- Be Cautious of Phishing and Scams: Always be wary of unsolicited emails, messages, or phone calls asking for personal information. Verify the authenticity of the source before responding, and avoid clicking on links or downloading attachments from unknown senders. Recognizing and avoiding phishing attempts can significantly reduce the risk of falling victim to scams.
By following these steps, individuals can better protect their personal information from cyber threats and mitigate the impact of potential data breaches. In an increasingly digital world, staying informed and proactive is essential to maintaining security and trust.

