Escalation of Cyber Warfare in the Israel-Palestine Conflict: A Deep Dive into Recent Israeli Breaches
The geopolitical conflict between Israel and its adversaries has shifted into the digital sphere, where sophisticated cyberattacks have become a primary tool for targeting critical sectors. In recent months, cyberattacks have exposed Israeli defense data, diplomatic communications, and sensitive civilian information. Among the prominent players in this cyberwarfare is the Handala Group, a hacktivist entity leveraging advanced persistent threat (APT) tactics to disrupt Israeli operations. Other actors, such as EagleStrike and the Hunter Killer hacker group, further complicate Israel’s cybersecurity landscape.
This blog analyzes recent Israeli breaches, the types of data compromised, and the strategic implications of these attacks, offering insights into the evolving digital conflict.
Handala’s Cyber Campaign: Recent Breaches Targeting Israel
In the past few months, Handala has launched a series of attacks across various sectors in Israel, targeting critical infrastructure, government entities, and individual high-profile figures.
1. Doscast Hacked (October 10, 2024)
Handala targeted Doscast, a major audio platform for the ultra-Orthodox Jewish community. This attack disrupted the platform, which hosts a variety of commentators and conversationalists, exposing its vulnerabilities and impacting its wide user base. The symbolic nature of this hack underscores Handala’s ideological objectives, as Doscast is a prominent site within the religious community.
2. Ambassador of Israel in Germany Emails (October 8, 2024)
Handala compromised 50,000 emails from Ron Prosor, the Israeli Ambassador to Germany and former senior Mossad officer. The leaked emails expose sensitive diplomatic communications, potentially affecting Israel’s foreign relations. This breach also highlights Handala’s aggressive tactics, as they included personal threats against Prosor, claiming constant surveillance over his activities.
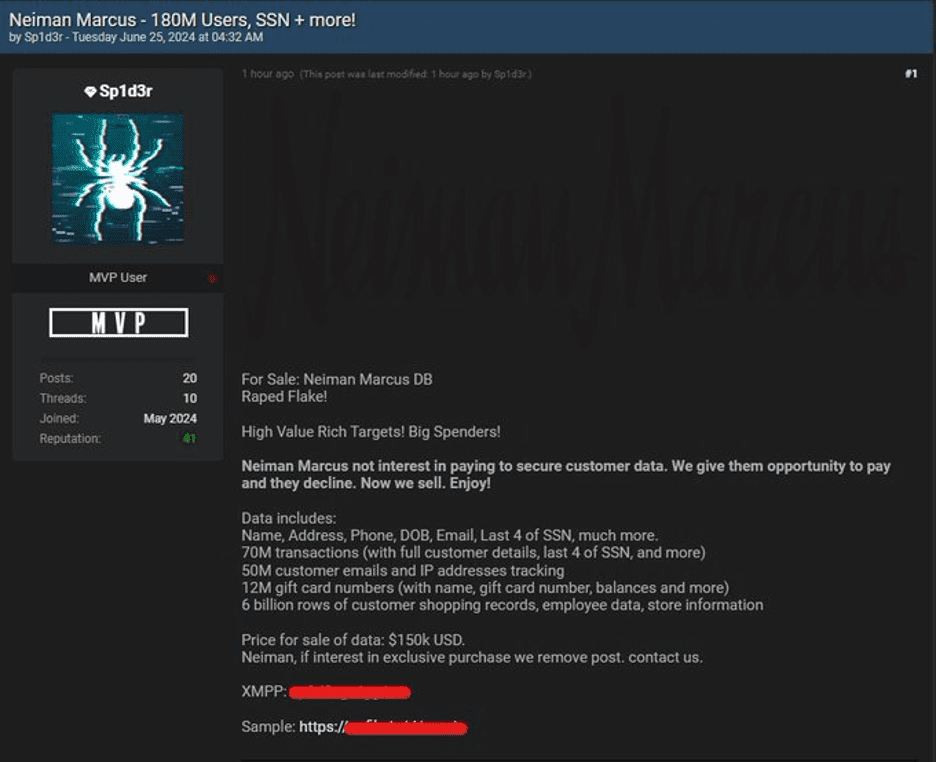
3. Max Shop Hacked (October 8, 2024)
The breach of Max Shop, a cloud-based terminal system used in over 9,000 stores, resulted in the theft of 1.5TB of data. The attack defaced store kiosks and sent threatening messages to 250,000 Israeli citizens. This attack directly impacted retail operations and exposed personal information, further heightening concerns over civilian data security.
4. Israeli Industrial Batteries (IIB) Leak (October 6, 2024)
Handala released 300GB of data from IIB (Israeli Industrial Batteries), a company involved in providing energy storage infrastructure to Israel’s military and defense sectors. The breach of IIB threatens the resilience of Israel’s defense logistics, particularly its energy-dependent military operations.
5. Shin Bet Hacked (October 3, 2024)
Handala successfully breached the Shin Bet’s security system, compromising their exclusive mobile security application used by officers. This attack poses a significant risk to Israel’s internal security, potentially exposing confidential communications, field agents, and counterterrorism operations.
6. Israeli Prime Minister Emails (October 2, 2024)
The group leaked 110,000 secret emails belonging to former Prime Minister Ehud Barak. Handala claims to have been surveilling Israel’s leadership for decades. This breach exposes sensitive government discussions, further undermining Israel’s internal political operations and national defense strategies.
7. Soreq Nuclear Research Center (September 28, 2024)
Handala targeted the Soreq Nuclear Research Center (NRC), a key nuclear research facility in Israel. The group claims to have stolen comprehensive data, including emails, infrastructure maps, personnel details, and administrative documents. This breach could severely compromise Israel’s nuclear capabilities and has far-reaching implications for national security.
8. Israeli Foreign Affairs Minister Emails (September 26, 2024)
Handala exposed 60,000 emails belonging to Gabi Ashkenazi, former Minister of Foreign Affairs and Chief of General Staff of the Israeli Armed Forces. The breach includes communications that could be used to disrupt Israel’s foreign policy initiatives, further eroding trust in the nation’s cybersecurity capabilities.
9. Benny Gantz Hacked (September 23-24, 2024)
Handala published 35,000 confidential emails and 2,000 private photos of Benny Gantz, the former Defense Minister. The group’s goal is not only to embarrass the official but to expose internal defense discussions. This breach is a significant escalation in the group’s attacks on individual high-profile figures, highlighting the personal risks involved for Israeli officials.
EagleStrike and the Hunter Killer Leak (September 2024)
On September 30, 2024, EagleStrike exposed a comprehensive data breach facilitated by the Hunter Killer group. The leak included critical Israeli state data, including:
- Israel MFA Access: Over 370GB of data from the Ministry of Foreign Affairs was compromised, including remote desktop access (RDP) and SharePoint credentials. This breach threatens Israeli diplomatic operations and international communications.
- Mossad Email Server Dump: 27,000 emails were leaked, revealing sensitive information from 2017 to 2023. This exposes Mossad’s covert operations and intelligence-gathering efforts, placing Israel’s security at significant risk.
- Defense Contractors: Data from Rafael Advanced Defense Systems and Elbit Systems was also part of the breach. Intellectual property and defense technology information were exposed, severely impacting Israel’s defense development.
- Military and SCADA Systems: Handala obtained access to 70 SCADA systems, which control critical infrastructure such as water and energy. The potential sabotage of these systems could lead to widespread service disruptions or worse, physical damage to key facilities.
Handala’s Extortion Tactics and Ransomware Campaigns
Handala is not only focused on cyber sabotage but also engages in ransomware and extortion, often targeting high-value industries. Notable ransomware campaigns include:
- Healthcare Sector (February – June 2024): Handala targeted hospitals and healthcare organizations, demanding 8 BTC (~$569,252 USD) in ransom. This campaign involved the theft of patient records and financial data, crippling healthcare operations.
- Defense and IT Sectors (March – May 2024): Handala launched coordinated attacks on Israel’s defense contractors and IT services. These breaches exposed proprietary technologies and military secrets, undermining Israel’s defense infrastructure.
Extortion Methods: Handala’s extortion model involves leaking data through Clearnet and TOR sites, alongside Telegram channels, if ransom demands are not met. These platforms enable Handala to continuously publicize their exploits and pressure victims.
Impacts on Israeli Citizens: Identity Theft and Civil Disruptions
While the breaches targeting government and military entities are alarming, Handala has increasingly targeted civilians, amplifying public concern over data security.
Max Shop Hack (October 2024)
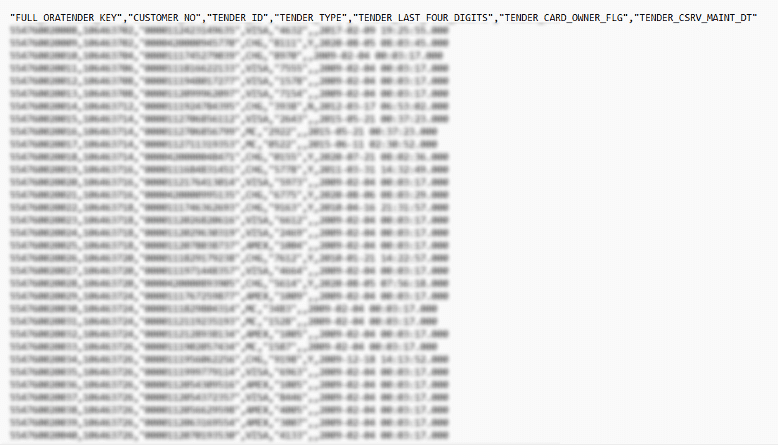
This attack affected over 9,000 retail systems across Israel, leaking 1.5TB of personal and financial data from 250,000 Israeli citizens. Beyond the direct financial losses, victims are vulnerable to identity theft and phishing schemes. The hack demonstrates Handala’s capacity to disrupt civilian life and further erodes public trust in data security.
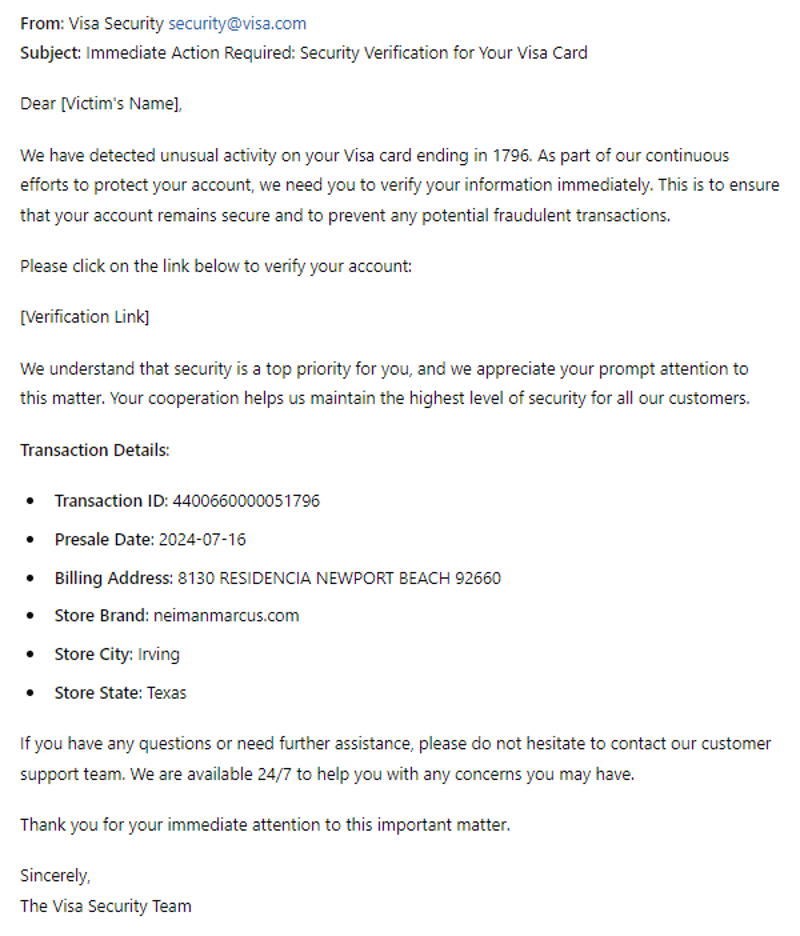
Identity Theft and Phishing Risks:
- Financial Loss: Stolen identities can be used to open fraudulent bank accounts and apply for credit.
- Phishing Campaigns: Detailed personal data enables highly targeted phishing attacks, further compromising individual security.
- Long-term Privacy Concerns: Once personal data circulates on dark web markets, it remains accessible, prolonging the risk of exploitation.
Conclusion
Handala’s cyber campaigns against Israel mark a significant escalation in digital warfare. Their attacks on critical infrastructure, defense systems, and civilian sectors have exposed substantial vulnerabilities. These breaches not only undermine Israel’s national security and diplomatic standing but also pose severe risks to individual citizens through identity theft and financial fraud.
Israel must implement a multi-layered defense strategy that includes strengthening its cybersecurity infrastructure, enhancing public awareness, and fostering international cooperation. With adversaries like Handala continuing to innovate their tactics, robust defense measures are essential to safeguard the nation’s critical assets and its people.